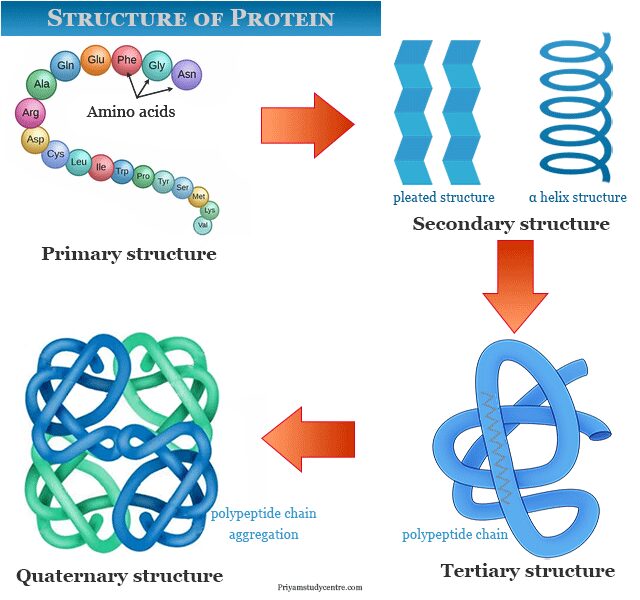
Protein Structure Hierarchy . to determine how the protein gets its final shape or conformation, we need to understand these four levels of protein. this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. a protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. Proteins can be divided into two categories: the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. The complexity of protein structures requires a description of their structural components.
from www.priyamstudycentre.com
The complexity of protein structures requires a description of their structural components. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which. a protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines. Proteins can be divided into two categories: to determine how the protein gets its final shape or conformation, we need to understand these four levels of protein.
Protein Definition, Classification, Structure
Protein Structure Hierarchy this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. The complexity of protein structures requires a description of their structural components. the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which. to determine how the protein gets its final shape or conformation, we need to understand these four levels of protein. this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. a protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. Proteins can be divided into two categories: Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure.
From www.priyamstudycentre.com
Protein Definition, Classification, Structure Protein Structure Hierarchy The complexity of protein structures requires a description of their structural components. Proteins can be divided into two categories: the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines. a protein can be identified based on each level of its structure.. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION Overview of protein structure hierarchy Studypool Protein Structure Hierarchy the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines. this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. a protein can be identified based. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins PowerPoint Presentation Protein Structure Hierarchy a protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. Proteins can be divided into two categories: . Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www.scribd.com
Protein Structure Hierarchy of Protein Structure Amino Acid 2 Distinct Protein Structure Hierarchy the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. a protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. Proteins can be divided into two categories: The. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www.medschoolcoach.com
Levels of Protein Structure MCAT Biochemistry MedSchoolCoach Protein Structure Hierarchy the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. The complexity of protein structures requires a description of their structural components. Proteins can be divided into two categories: this. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From biologydictionary.net
Protein Structure Biology Dictionary Protein Structure Hierarchy The complexity of protein structures requires a description of their structural components. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which. to determine how the protein gets its final shape or conformation,. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION Overview of protein structure hierarchy Studypool Protein Structure Hierarchy Proteins can be divided into two categories: to determine how the protein gets its final shape or conformation, we need to understand these four levels of protein. a protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary,. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Proteins PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4413605 Protein Structure Hierarchy Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. Proteins can be divided into two categories: this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. to determine how the protein gets its final shape or conformation, we need to understand these four levels of protein. the primary structure of a protein. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Conditional Graphical Models for Protein Structure Prediction Protein Structure Hierarchy Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which. the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines. this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. a protein can be identified based. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www.docsity.com
Protein Structure Hierarchy Lecture Slides BCH 401G Docsity Protein Structure Hierarchy Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which. a protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain,. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Principles of protein structure and stability. PowerPoint Protein Structure Hierarchy the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines. to determine how the protein gets its final shape or conformation, we need to understand these four levels of protein. Proteins can be divided into two categories: The complexity of protein. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION Overview of protein structure hierarchy Studypool Protein Structure Hierarchy the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines. this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which. The complexity of protein structures requires a. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www2.victoriacollege.edu
4 levels of protein structure Protein Structure Hierarchy Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which. to determine how the protein gets its final shape or conformation, we need to understand these four levels of protein. this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. Proteins can be. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From mavink.com
4 Levels Of Protein Structure Protein Structure Hierarchy this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. a protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines. Fibrous, which tend to be. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www.researchgate.net
1 Protein structure hierarchy. The illustrated protein is an arsenate Protein Structure Hierarchy to determine how the protein gets its final shape or conformation, we need to understand these four levels of protein. this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. The complexity of protein structures requires a description of their structural components. a. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From wellcomecollection.org
Hierarchical organizatn. of protein structur Collection Protein Structure Hierarchy Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which. a protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. The complexity of protein structures requires a description of their structural components. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www.researchgate.net
3. The four hierarchical levels of the protein structure. Used with Protein Structure Hierarchy Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. The complexity of protein structures requires a description of their structural components. the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines. Proteins can be divided into two categories: to. Protein Structure Hierarchy.
From www.mun.ca
Four levels of Protein Structure Protein Structure Hierarchy this overview provides an illustrated, comprehensive survey of some commonly observed protein‐fold families. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which. Proteins can be divided into two categories: the primary structure of a protein — its amino acid sequence — drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines.. Protein Structure Hierarchy.